| Why is Calcitriol better than Vitamin D? |
| |
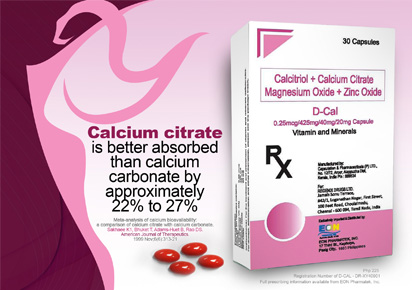
| D-Cal: a combined vitamin D and calcium supplement; is recommended for all women at increased risk of fracture, osteoporosis and those who developed osteoporosis. |
 |
| THE ROLE OF CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D IN THE MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS |
| R. Rizzolia,⁎, S. Boonenb, M.L. Brandic, N. Burletd, P. Delmase, J.Y. Reginsterf
a Division of Bone Diseases, World Health Organization Collaborating Center for Osteoporosis Prevention, Department of Rehabilitation and Geriatrics, University Hospitals and Faculty of Medicine, 1211 Geneva 14, Switzerland b Leuven University Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases & Division of Geriatric Medicine, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Belgium c Department of Internal Medicine, University of Florence, Italy d International Osteoporosis Foundation, Switzerland e INSERM Research Unit 831 and Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Lyon, France f On behalf of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO), Belgium
|
| |
| Introduction |
| Osteoporosis is a chronic, progressive bone disease in which bone resorption exceeds bone formation, leading to a reduction in bone mineral density and disruption of bone microarchitecture. Patients with osteoporosis have an increased risk of fractures that occur with stresses which would not normally cause fracture in a non-osteoporotic individual. |
| |
 |
The incidence of osteoporosis increases with age and occurs most frequently in postmenopausal women because the decrease in ovarian oestrogen associated with the menopause accelerates bone loss and increases bone remodelling [1]. Many studies have investigated the effect of vitamin D and calcium supplements on osteoporosis and fracture risk in postmenopausal women. A round table discussion was held between experts in order to reach a consensus on a number of issues regarding the use of dietary supplements of vitamin D and calcium in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. |
|
| |
| Majority of studies that have investigated the effects of combined calcium and vitamin D supplementation in postmenopausal women have shown a reduction in fracture risk, providing that sufficient patient compliance (75–80%) was reached. The panel's consensus was that supplementation with calcium and vitamin D should be recommended in women at increased risk of osteoporosis and those who have developed osteoporosis. In the case of vitamin D, the dose given should be enough to ensure that circulating levels of 25(OH)D reach the threshold of 50 nmol/l. |
| |
Since calcium and vitamin D supplementation should be targeted to those individuals at increased risk of fracture and since age is a very important determinant of fracture risk, a target for intervention in the elderly, particularly those over 65 years. The need for dietary supplementation with calcium and vitamin D may be increased in the elderly for a number of reasons.
|
 |
|
Is there any interest to adding calcium to vitamin D supplementation or adding vitamin D to calcium supplementation?
Many studies have shown that persistence and compliance with supplementation regimens can be low, and that poor compliance impairs efficacy. It is necessary therefore, from both an efficacy and a health economic perspective, to ensure that any dosing regimen is designed with this in mind. Where medically appropriate, combination treatments may improve treatment compliance by reducing the number of medications which patients need to take.
Current evidence suggests the role that calcium and vitamin D play in fracture prevention is not attributable to calcium alone and a meta-analysis of data from 9 randomized clinical trials, including a total of 53,260 patients, found that where the effects of supplementation with vitamin D alone were explored (in a total of 9038 patients), this was not sufficient to significantly reduce the risk of hip fracture in postmenopausal women [6]. However the same study found that combined supplementation with vitamin D and calcium reduced the risk of hip fracture by 25% (95% CI: 4–42) and the risk of nonvertebral fracture by 23% (95% CI: 1–40) compared to supplementation with vitamin D alone. The meta-analysis estimated the number needed to treat (NNT) to prevent one adverse outcome to be 276 (95% CI: 165–843) for hip fractures and 72 (95% CI: 35–834) for non-vertebral fractures. These results support a previous meta-analysis which has shown a reduction of 19%( 95%CI:4–32) for hip fracture and of 13% (95% CI: 3–22) for any non-vertebral fracture.
Conclusion
Supplementation with calcium and vitamin D can be justified both in terms of efficacy and health economics in women at increased risk of osteoporotic fracture, including those who have not yet sustained a fracture. Women can be considered to be at increased risk of fracture if they are over 65 years of age, or; if osteopenic and/or with proven calcium and/or vitamin D insufficiency when they are younger. Evidence suggests that for the greatest reduction in fracture risk, women at increased risk should be given both calcium and vitamin D supplements, in the order of 1000–1200 mg calcium (depending on baseline status)and 800IU vitamin D daily. Combining vitamin D and calcium into one supplement is recommended as this may increase patient adherence, which in turn improves overall efficacy. In conclusion, combined vitamin D and calcium supplementation is recommended for all women at increased risk of fracture, including those also taking other anti-osteoporostic treatments. |
Reference
Bone 42 (2008) 246–249
www.elsevier.com/locate/bone |
| |
|
 |
|